Types of Soil Tests
Learn about the different ways soil can be tested. Western agriculture has been fixated on the chemical composition, but there's much more!
Soil compaction occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space and creating dense, hard soil layers. This restricts...
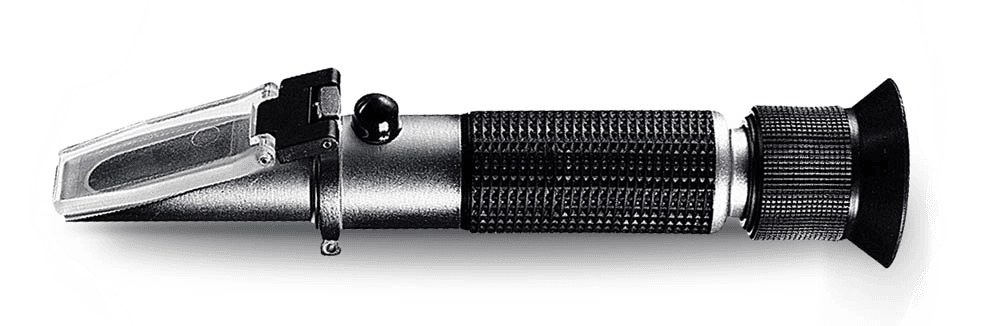
BRIX is a measure of the sugar content in plant sap, which indicates the overall health and nutri...
Phospholipid Fatty Acid (PLFA) analysis provides a snapshot of the soil microbial community structure and biomass. It helps identify the ...
NPK analysis measures the three primary macronutrients in soil: Nitrogen (N), Phosphoru...
No video available
Upload microscope recording
Soil microscopy analysis examines the physical structure and biological components of soil under ...
The carbon to nitrogen (C:N) ratio measures the balance between carbon and nitrogen in soil organic matter. This ratio is crucial for microbial activity...